Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders affecting women of reproductive age, with an estimated prevalence ranging from 2.2% to 26% globally. This complex endocrine condition affects multiple body systems and requires comprehensive understanding for effective management. Despite its prevalence, the World Health Organization estimates that up to 70% of women with PCOS remain undiagnosed, highlighting the critical need for awareness and education.kansashealthsystem+2
Anatomical diagram of polycystic ovary syndrome showing multiple cysts on ovaries
Understanding PCOS: The Fundamentals
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
PCOS is a multifaceted hormonal disorder that primarily affects the ovaries, the reproductive organs responsible for producing estrogen, progesterone, and small amounts of male hormones called androgens. The condition is characterized by an imbalance of reproductive hormones, leading to various symptoms that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life.healthline
The name “polycystic ovary syndrome” can be misleading, as it suggests the condition is solely about the ovaries. However, PCOS is actually a full-body endocrine and metabolic disorder that affects multiple organ systems. The “cysts” referenced in the name are actually immature follicles containing eggs that never mature enough to trigger ovulation.helloclue+1
The Three Main Features of PCOS
According to current medical understanding, PCOS presents three primary characteristics:healthline
1. Cysts in the Ovaries: Multiple small, fluid-filled sacs develop inside the ovaries. These are actually follicles containing immature eggs that fail to mature sufficiently to trigger ovulation.
2. High Levels of Androgens: The ovaries produce excessive amounts of male hormones (androgens), which interfere with normal ovulation and can cause various physical symptoms.
3. Lower Levels of Progesterone: The absence of regular ovulation disrupts the normal balance of reproductive hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and other key hormones.
PCOS Diagnosis: The Rotterdam Criteria
The diagnosis of PCOS has evolved significantly over the decades. Currently, healthcare providers use the Rotterdam Criteria, established in 2003, which remains the most widely accepted diagnostic standard.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Diagnostic Requirements
PCOS diagnosis requires the presence of at least two out of three key features:pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
1. Clinical or Biochemical Hyperandrogenism
- Excess facial and body hair (hirsutism) with modified Ferriman-Gallwey score ≥4 to ≥8
- Elevated total or free testosterone levels
- Severe acne or male-pattern baldness
2. Ovulatory Dysfunction
- Irregular menstrual cycles (cycles >35 days apart or <8 menses per year)
- Absent periods (amenorrhea)
- Evidence of anovulation through hormone testing
3. Polycystic Ovarian Morphology
- ≥20 follicles per ovary visible on transvaginal ultrasound
- Ovarian volume ≥10 cm³
- Based on high-quality ultrasound with transducer frequency ≥8 MHz
Exclusion of Other Conditions
Before confirming a PCOS diagnosis, healthcare providers must exclude other conditions that can mimic PCOS symptoms, including:academic.oup
- Thyroid disorders
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Cushing syndrome
- Androgen-secreting tumors
Common Symptoms and Their Impact
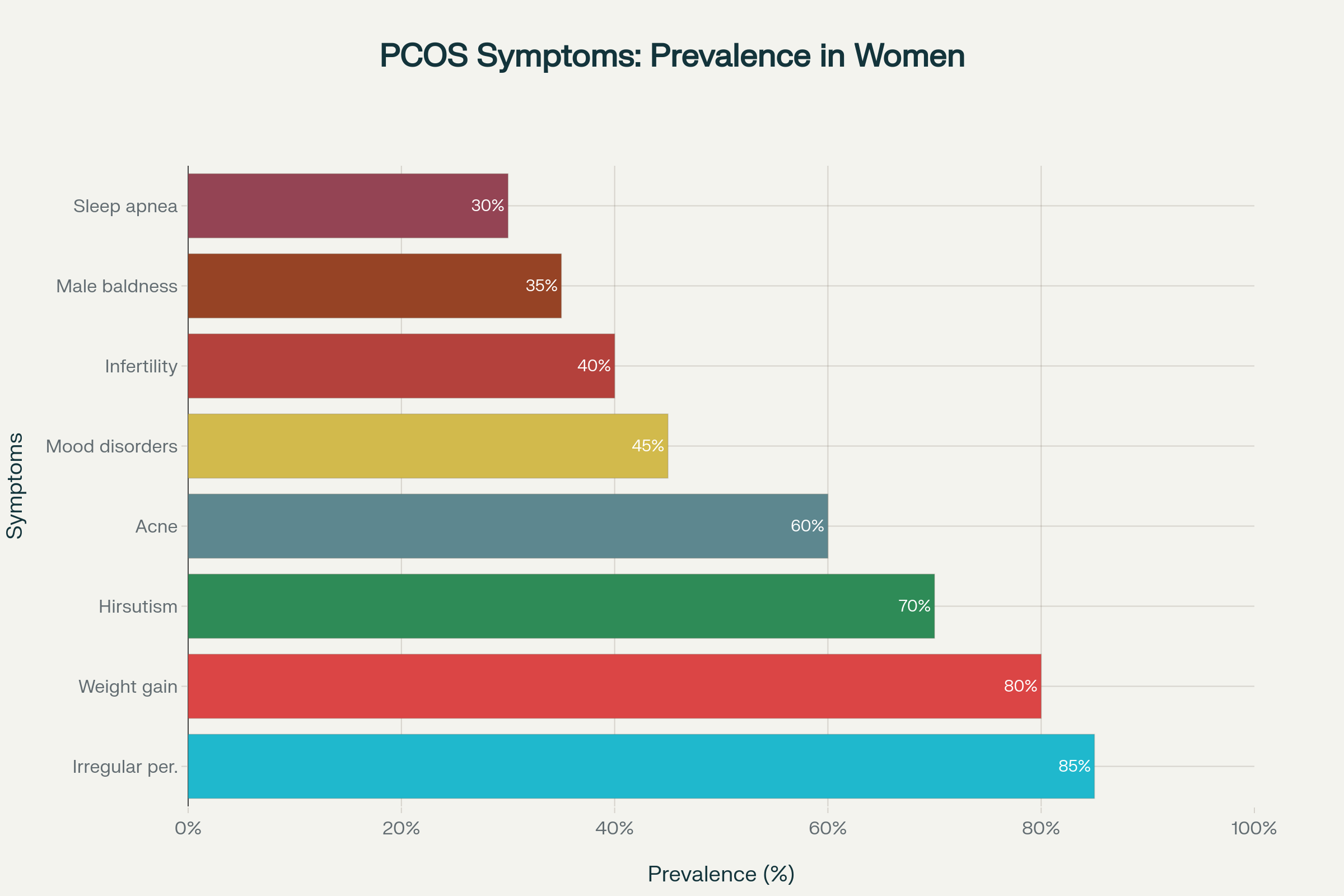
Prevalence of common PCOS symptoms in women diagnosed with the condition
Primary Physical Symptoms
Irregular or Absent Periods: This is the most common symptom, affecting approximately 85% of women with PCOS. Women may experience fewer than eight periods per year or no periods at all due to irregular or absent ovulation.kansashealthsystem+1
Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism): Up to 70% of women with PCOS develop unwanted hair growth on the face, chest, back, and other typically male-pattern areas. This occurs due to elevated androgen levels.healthline+1
Acne and Oily Skin: Male hormones can make skin oilier than usual, leading to acne breakouts on the face, chest, and upper back. Adult acne can be a significant indicator of hormonal imbalance.healthline
Weight Gain and Difficulty Losing Weight: Approximately 80% of women with PCOS struggle with weight management. The condition often involves insulin resistance, making weight loss particularly challenging.healthline
Male-Pattern Baldness: Hair thinning or loss from the scalp affects about 35% of women with PCOS, occurring due to elevated androgen levels.kansashealthsystem
Secondary Symptoms and Complications
Fertility Issues: PCOS is one of the leading causes of female infertility, affecting approximately 40% of women with the condition. Irregular or absent ovulation makes conception difficult without medical intervention.nhs+1
Skin Changes: Dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans) can develop in body creases such as the neck, groin, and under the breasts, often indicating insulin resistance.healthline
Sleep Disorders: Women with PCOS have higher rates of sleep apnea, a condition causing interrupted breathing during sleep, leading to daytime fatigue.kansashealthsystem
Mood Changes: Hormonal imbalances can trigger headaches and contribute to mood swings, anxiety, and depression.kansashealthsystem+1
The Role of Insulin Resistance in PCOS
Understanding Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a key feature of PCOS, affecting 65-95% of women with the condition. In women with obesity and PCOS, the prevalence reaches 70-80%, while 20-25% of lean women with PCOS also experience insulin resistance.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
With insulin resistance, the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, requiring the pancreas to produce increasingly higher amounts of this hormone to maintain normal blood sugar levels. This creates a cascade of hormonal disruptions that worsen PCOS symptoms.helloclue+1
How Insulin Resistance Affects PCOS
Androgen Production: Excess insulin stimulates the ovaries to produce more male hormones (androgens), worsening symptoms like hirsutism and acne.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Weight Gain: High insulin levels promote fat storage and make weight loss extremely difficult. This creates a vicious cycle, as excess weight further increases insulin resistance.nhs
Ovulation Disruption: Elevated insulin interferes with normal ovarian function, preventing regular ovulation and leading to irregular periods.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Inflammation: Insulin resistance contributes to chronic, low-grade inflammation throughout the body, which can worsen PCOS symptoms and increase long-term health risks.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
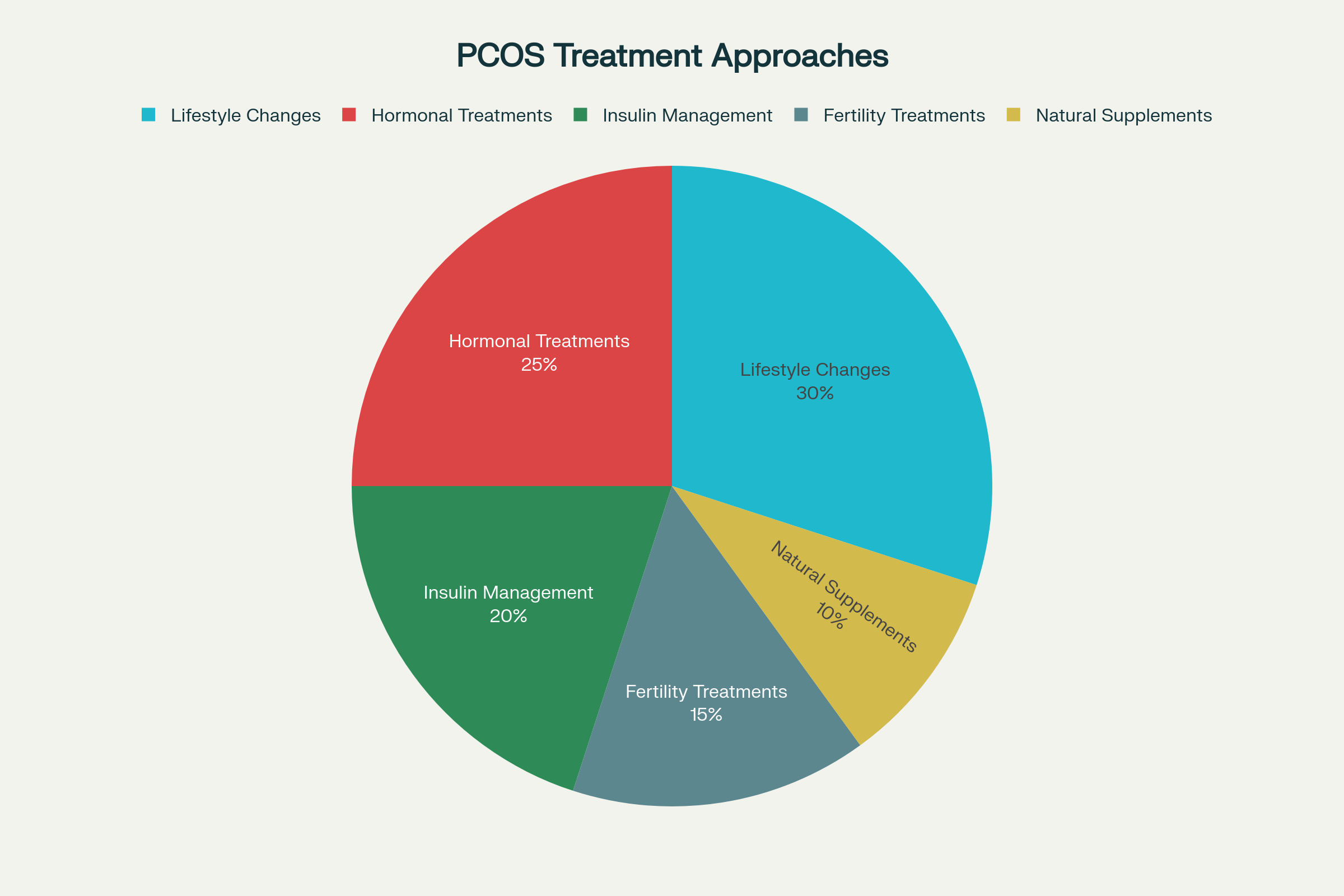
Distribution of different PCOS treatment approaches commonly used in clinical practice
Lifestyle Modifications: The Foundation of PCOS Management
Dietary Changes form the cornerstone of PCOS treatment. Research consistently shows that appropriate nutrition can significantly improve symptoms and long-term health outcomes.drdanielkushner+2
Recommended Dietary Strategies
Low Glycemic Index Foods: Choose foods that cause gradual rises in blood sugar rather than sharp spikes. Examples include:bda.uk+1
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
- Non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, peppers)
- Berries and other low-sugar fruits
High-Fiber Foods: Fiber helps slow digestion and reduces insulin spikes. Aim for 21-25 grams daily from sources like:healthline+1
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower)
- Leafy greens (kale, spinach, arugula)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds)
- Whole grains and legumes
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Include foods that help reduce chronic inflammation:healthline
- Fatty fish rich in omega-3s (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Olive oil and avocados
- Colorful fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Refined Carbohydrates: These cause rapid blood sugar spikes and worsen insulin resistance:webmd+1
- White bread, pastries, and baked goods
- Sugary cereals and processed snacks
- White rice and regular pasta
- Sugary drinks and fruit juices
Processed Foods: High in unhealthy fats, sodium, and additives that can worsen inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.healthline

PCOS-friendly foods including leafy greens, berries, whole grains, and lean proteins
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for PCOS management, offering multiple benefits:drdanielkushner+1
Cardiovascular Exercise: Helps burn calories, improve insulin sensitivity, and support weight management. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
Strength Training: Builds muscle mass, which improves metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Include resistance exercises 2-3 times per week.
Flexibility and Stress Reduction: Activities like yoga and stretching can help manage stress, which often worsens PCOS symptoms.
Medical Treatments
Hormonal Therapies
Birth Control Pills: Often the first-line treatment for women not trying to conceive. Benefits include:aafp+1
- Regulating menstrual cycles
- Reducing androgen levels
- Improving acne and hirsutism
- Protecting against endometrial cancer
Anti-Androgen Medications: Such as spironolactone, can help reduce excessive hair growth and acne by blocking the effects of male hormones.nichd.nih
Insulin Management
Metformin: Originally developed for diabetes, this medication helps improve insulin sensitivity and is widely used in PCOS treatment. Benefits include:healthline+1
- Improved insulin levels and glucose metabolism
- Enhanced menstrual regularity
- Support for weight management
- Reduced risk of diabetes progression
Fertility Treatments
For women trying to conceive, several options are available:advancedfertility+2
Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid): The most common first-line fertility treatment, with approximately 15% monthly success rate when ovulation occurs.advancedfertility
Letrozole (Femara): Recent studies suggest letrozole may be more effective than clomiphene for inducing ovulation in women with PCOS.aafp+1
Injectable Gonadotropins: For women who don’t respond to oral medications, with approximately 20% monthly success rate.advancedfertility
Ovarian Drilling: A surgical procedure that can help restore ovulation in up to 80% of cases.fertilitynj
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): The most effective option with approximately 60% success rates at specialized clinics.advancedfertility
Natural Supplements and Alternative Therapies
Evidence-Based Supplements
Inositol: Particularly myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and hormone balance. Studies show benefits with 2-4 grams daily for 3-6 months.goodrx+1
Berberine: This plant compound can improve insulin resistance, reduce androgen levels, and support weight management. Typical dosing ranges from 400-1500mg daily.health+1
Chromium: Helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, with chromium picolinate being the preferred form.goodrx+1
Vitamin D: Many women with PCOS are deficient in vitamin D. Supplementation, especially when combined with calcium, can improve menstrual regularity and ovulation.vinmec+1
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help reduce inflammation and may improve metabolic parameters. Include fatty fish or high-quality fish oil supplements.bda.uk+1
Herbal Remedies
Cinnamon: May help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce testosterone levels. Studies suggest 1,500mg daily for 6-24 weeks.health+1
Turmeric (Curcumin): Offers anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce insulin resistance. Typical dosing is 500-1500mg daily.vinmec+1
Adaptogenic Herbs: Such as ashwagandha, maca root, and holy basil may help balance hormones and reduce stress.vinmec
Mental Health and PCOS
The Psychological Impact
PCOS significantly affects mental health, with women experiencing:pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
Depression: Women with PCOS are 2.79 times more likely to be diagnosed with depression compared to women without the condition.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih
Anxiety: The risk of anxiety disorders is 2.75 times higher in women with PCOS.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih
Body Image Issues: Physical symptoms like weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth can severely impact self-esteem and body image.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Quality of Life: The combination of physical symptoms and fertility concerns can significantly reduce overall quality of life.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Coping Strategies
Professional Support: Consider counseling or therapy to address the emotional aspects of living with PCOS.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Support Groups: Connect with other women experiencing similar challenges through online or in-person support groups.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.bda.uk
Body Positivity: Focus on what your body can do rather than just appearance, and celebrate small improvements in symptoms.
Long-Term Health Risks and Complications
Metabolic Complications
Type 2 Diabetes: Women with PCOS have a significantly increased risk of developing diabetes due to insulin resistance.who+2
Cardiovascular Disease: PCOS is associated with increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels.uchicagomedicine+2
Metabolic Syndrome: The combination of insulin resistance, obesity, and hormonal imbalances increases the risk of metabolic syndrome.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Reproductive Health Risks
Endometrial Cancer: Due to irregular ovulation and prolonged exposure to estrogen without progesterone, women with PCOS have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.who+2
Pregnancy Complications: Women with PCOS face higher risks of:pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
- Gestational diabetes (threefold increased risk)
- Pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia
- Preterm delivery
- Complications during delivery
Other Health Concerns
Sleep Apnea: Higher prevalence of sleep disorders can affect overall health and quality of life.uchicagomedicine
Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is more common in women with PCOS.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Cancer Risk: Some studies suggest increased risks of breast and ovarian cancer, though more research is needed.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Creating a Comprehensive Management Plan
Working with Healthcare Providers
Multidisciplinary Approach: PCOS management often requires a team including:
- Gynecologist or endocrinologist
- Registered dietitian
- Mental health counselor
- Fertility specialist (if needed)
Regular Monitoring: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor:asrm
- Blood glucose and insulin levels
- Lipid profiles and cardiovascular markers
- Thyroid function
- Blood pressure
- Mental health screening
Personalized Treatment Strategy
Identify Priorities: Determine your main concerns (fertility, weight management, symptom control) to guide treatment decisions.
Lifestyle First: Implement dietary and exercise changes as the foundation of your management plan.
Medication When Needed: Work with your healthcare provider to determine if medications are necessary to achieve your goals.
Monitor Progress: Track symptoms, menstrual cycles, and other relevant markers to assess treatment effectiveness.
Future Outlook and Emerging Treatments
Research Developments
Scientists continue to investigate new treatment approaches for PCOS, including:
- Novel insulin-sensitizing medications
- Targeted hormone therapies
- Genetic research to understand underlying causes
- Personalized medicine approaches based on individual PCOS phenotypes
Hope for the Future
While PCOS is a chronic condition, the outlook for women with this syndrome continues to improve. With proper management, most women can successfully control their symptoms, maintain good health, and achieve their reproductive goals.
Conclusion
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a complex but manageable condition affecting millions of women worldwide. Understanding the multifaceted nature of PCOS—from its hormonal imbalances and metabolic effects to its impact on mental health—is crucial for effective management.
The key to successful PCOS management lies in a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle modifications, appropriate medical treatments, and ongoing support. While the journey with PCOS can be challenging, with proper care and management, women can lead healthy, fulfilling lives and achieve their personal and reproductive goals.
Early diagnosis, consistent treatment, and regular monitoring are essential for preventing long-term complications and maintaining optimal health. Remember that PCOS management is highly individualized—what works for one woman may not work for another, making it crucial to work closely with knowledgeable healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers for proper diagnosis and treatment of PCOS or any other medical condition.
/weight-loss-diet-for-pcod-complete-diet-chart-meal-plan-2025