Introduction to Follicular Study
Infertility is a growing challenge, affecting nearly 15% of couples worldwide. One of the most trusted diagnostic tools in fertility medicine is the follicular study, also known as a follicular scan, follicular monitoring, or ovulation study.
This procedure uses a series of ultrasound scans across a woman’s menstrual cycle to monitor the growth and rupture of ovarian follicles and the readiness of the uterine lining. By analyzing a follicular study report, doctors can pinpoint the exact time of ovulation, thereby improving the chances of conception—whether naturally, through IUI, or via IVF.
Unlike ovulation kits or calendar-based predictions, a follicular ultrasound offers a real-time view of ovarian activity, making it the most accurate way to track fertility.
What is a Follicular Study?
A follicular study test involves tracking the development of ovarian follicles—the tiny sacs inside the ovary where eggs mature. During a typical menstrual cycle, one follicle becomes dominant, grows, and eventually ruptures to release an egg (ovulation).
Doctors use follicular scans to monitor:
- Follicle growth patterns
- Endometrial thickness (uterine lining)
- Ovulation timing (follicle rupture)
👉 Usually, 4–6 ultrasound scans are required in a cycle to complete the study.
Why is a Follicular Study Important?
1. In Natural Conception
For couples struggling with infertility or irregular periods, a follicular scan helps identify the fertile window, increasing chances of pregnancy.
2. In Assisted Reproductive Treatments
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): Ensures sperm insertion is timed exactly with ovulation.
- IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization): Determines the best day for egg retrieval and prevents premature ovulation.
3. In Hormonal Disorders
Conditions like PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) often cause irregular ovulation. A follicular monitoring report can help doctors design the right treatment plan.
The Science Behind Follicular Growth
Understanding Ovarian Follicles
Ovarian follicles are fluid-filled sacs inside the ovaries. Each cycle, several follicles begin to develop, but usually, only one matures and releases an egg.
Hormonal Regulation
- FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone): Encourages follicle development.
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Triggers ovulation when the follicle reaches maturity.
- Estrogen & Progesterone: Prepare the uterine lining for implantation.
Natural vs. Stimulated Ovulation
- Natural Cycles: Follicles grow on their own.
- Stimulated Cycles: Fertility drugs encourage multiple follicles, monitored via follicular ultrasound.
Follicular Study Procedure: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Baseline Scan (Day 2–3)
Checks for cysts, ovarian health, and initial follicle count.
Step 2: Growth Monitoring (Day 9–11)
Follicles are measured every 2–3 days. A day 11 follicle size of 14–16 mm is considered normal.
Step 3: Pre-Ovulation (Day 12–14)
The dominant follicle reaches 18–24 mm, signaling imminent ovulation.
Step 4: Ovulation Confirmation
Doctors check for follicle rupture and endometrium thickness (ET). A normal ET in follicular study is 8–12 mm.
👉 Most women undergo 4–6 follicular monitoring scans per cycle.
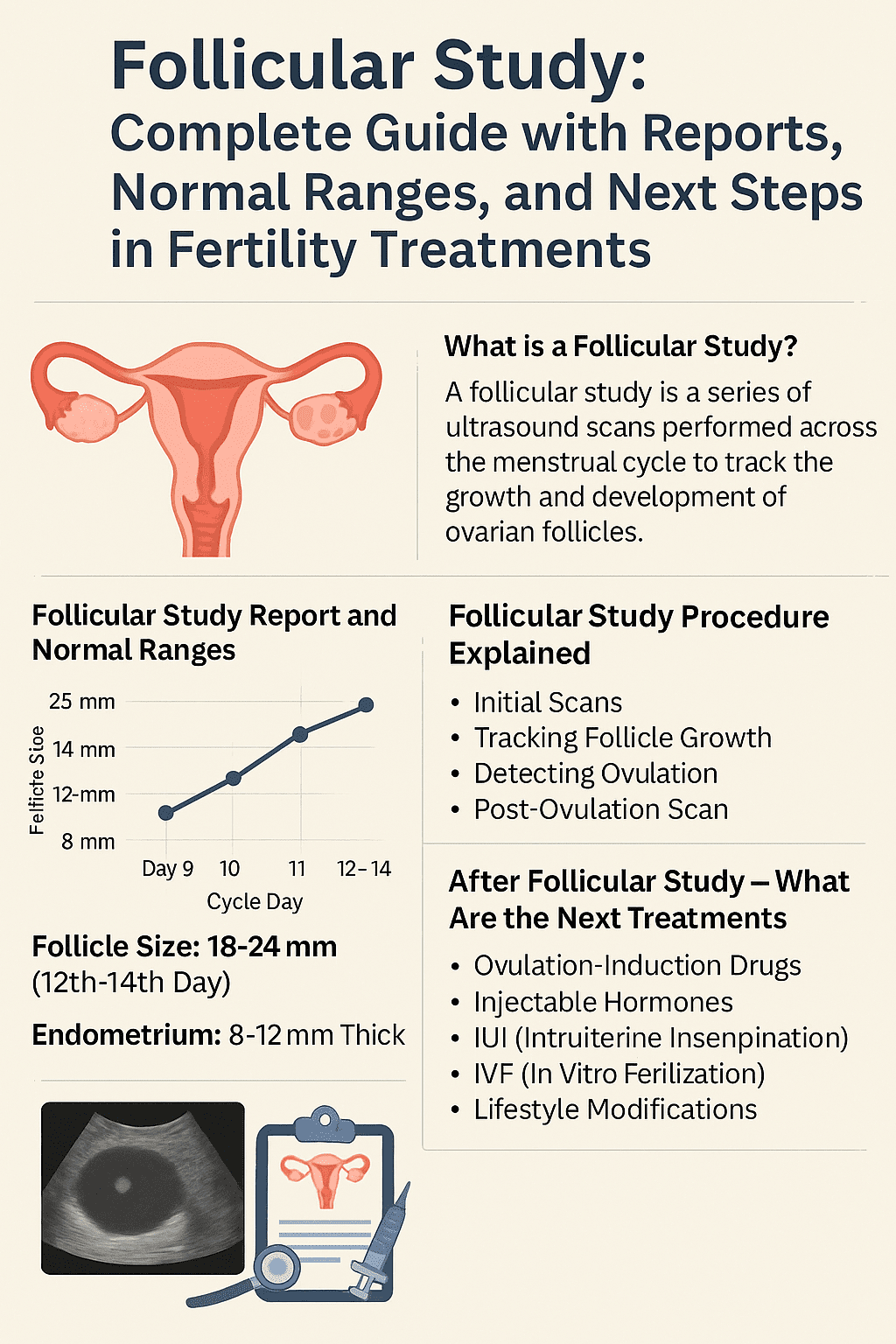
Follicular Study Report: Normal and Abnormal Findings
Normal Follicular Study Report
- Follicles grow steadily.
- Mature follicle reaches 18–24 mm.
- Endometrium thickness (ET): 8–12 mm.
- Follicle rupture observed → confirms ovulation.
Day-Wise Normal Follicle Size
- Day 9: 8–12 mm
- Day 10: 12–14 mm
- Day 11: 14–16 mm
- Day 12–14: 18–24 mm (ideal ovulation size)
Abnormal Reports
- Follicle grows but doesn’t rupture: Anovulation
- Multiple small follicles: PCOS
- Thin endometrium (<7 mm): Poor implantation chances
After Follicular Study – Next Treatments
If the follicular monitoring report shows irregular growth or failed ovulation, doctors may recommend:
- Ovulation-Inducing Medicines – Clomiphene Citrate, Letrozole.
- Hormonal Injections – FSH, hCG, or LH to stimulate follicles.
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) – If sperm motility is normal.
- IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization) – For more complex fertility issues.
- Lifestyle Modifications – Diet, weight management, and stress reduction.
👉 Learn more about advanced treatment options in our subpage: USG Follicular Study: Scan, Report & Price Explained (internal link).
Benefits of Follicular Monitoring
- Precise Ovulation Tracking – Eliminates guesswork.
- Boosts Conception Chances – For both natural and assisted methods.
- Customizable Treatment – Doctors adjust medication based on reports.
- Affordable First Step – Compared to advanced tests, follicular study price is lower.
Risks and Limitations
- Mild discomfort during transvaginal scans.
- Not a guarantee of pregnancy (other factors play a role).
- Emotional stress from repeated tests.
Cost of Follicular Study
India
- ₹800 – ₹3,000 per cycle
- Metro Cities: ₹1,500 – ₹3,500
Global Cost
- USA & Canada: $150 – $500
- UK & Europe: £100 – £300
- Asia (other than India): $50 – $200
👉 Compared to IVF, a follicular scan procedure is highly cost-effective.
FAQs on Follicular Study
1. How many times is follicular study done per cycle?
Usually 4–6 times, from Day 9 until ovulation is confirmed.
2. What is a normal follicle size on Day 11?
About 14–16 mm.
3. What does ET mean in follicular study?
ET refers to endometrial thickness, ideally 8–12 mm.
4. Can follicular study guarantee pregnancy?
No, but it improves timing accuracy, increasing chances.
5. Is follicular ultrasound painful?
No, though transvaginal scans may cause mild discomfort.
6. How much does follicular study cost?
In India, between ₹800 and ₹3,000 per cycle.
Conclusion
A follicular study (or follicular scan) is one of the most vital tools in reproductive medicine. By tracking follicle growth, ovulation timing, and uterine readiness, it provides actionable insights for couples trying to conceive.
Whether as part of natural conception, IUI, or IVF, this affordable and widely available test often marks the first step toward parenthood.
🔗 External References
- Ganesh Diagnostic – Follicular Study Test
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine – Ovulation Testing